Beer Making Equipment
Brewing beer at home is more than just a hobby—it’s an art, a science, and, let’s face it, a pretty cool way to impress your friends. But where do you start? The cornerstone of brewing success lies in understanding the tools of the trade. If you’re considering diving into the frothy world of homebrewing or setting up a commercial brewery, this guide on beer making equipment will walk you through everything you need to know—from essential tools to advanced brewing systems, costs, customization options, and beyond.
Overview of Beer Making Equipment
To brew beer, you need equipment that fits your brewing goals, whether you’re experimenting at home or scaling up for a craft brewery. Homebrewers often start with basic kits, while commercial brewers need sophisticated systems. Key considerations include capacity, equipment materials, and the process you intend to follow. Beer-making equipment can range from small-scale starter kits to elaborate setups with automated controls and industrial-grade stainless steel.
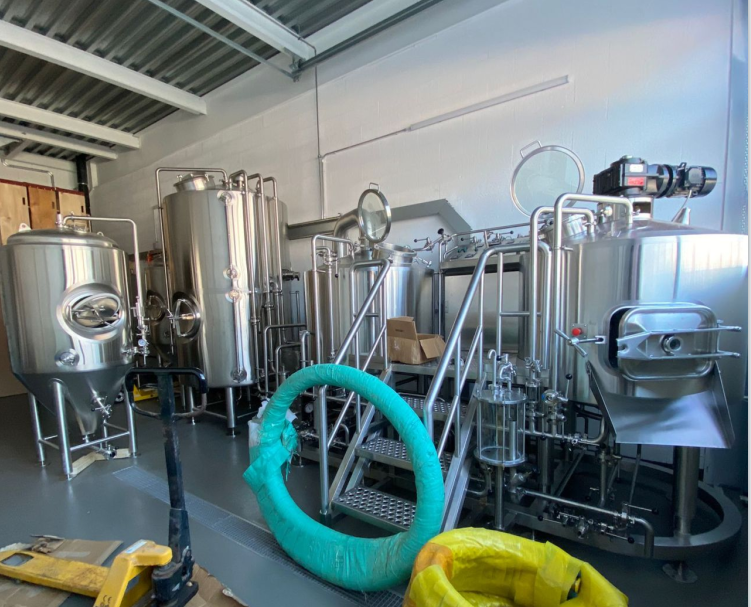

Essential Equipment Guide for Beer Making
Let’s break down the basic components of a brewing system and why each is important for creating that perfect pint.
1. Brewing Kettle
A brewing kettle is where the magic begins. It’s where you boil water, steep grains, and add hops. Look for one made of stainless steel for durability and even heat distribution. Copper kettles are pretty but tend to be more expensive.
2. Fermenter
Fermentation vessels are where yeast works its magic, turning sugars into alcohol. Homebrewers often use glass carboys or food-grade plastic buckets, while professional setups include conical stainless-steel fermenters for precise control.
3. Mash Tun
This insulated vessel is used for steeping and converting malted grains into wort. Home setups might use a converted cooler, while commercial systems include automated mash tuns with temperature controls.
4. Wort Chiller
After boiling, wort needs to cool quickly to avoid contamination. Immersion chillers, counterflow chillers, and plate chillers serve different needs depending on batch size and desired efficiency.
5. Hydrometer or Refractometer
Measuring the specific gravity of your beer is crucial for understanding fermentation progress and alcohol content. Hydrometers are affordable, while refractometers offer more precise readings.
6. Bottling and Kegging Equipment
When your beer is ready, you’ll need bottles, caps, cappers, or kegs to package your brew. For carbonation, many brewers use priming sugar for bottles or CO₂ systems for kegs.
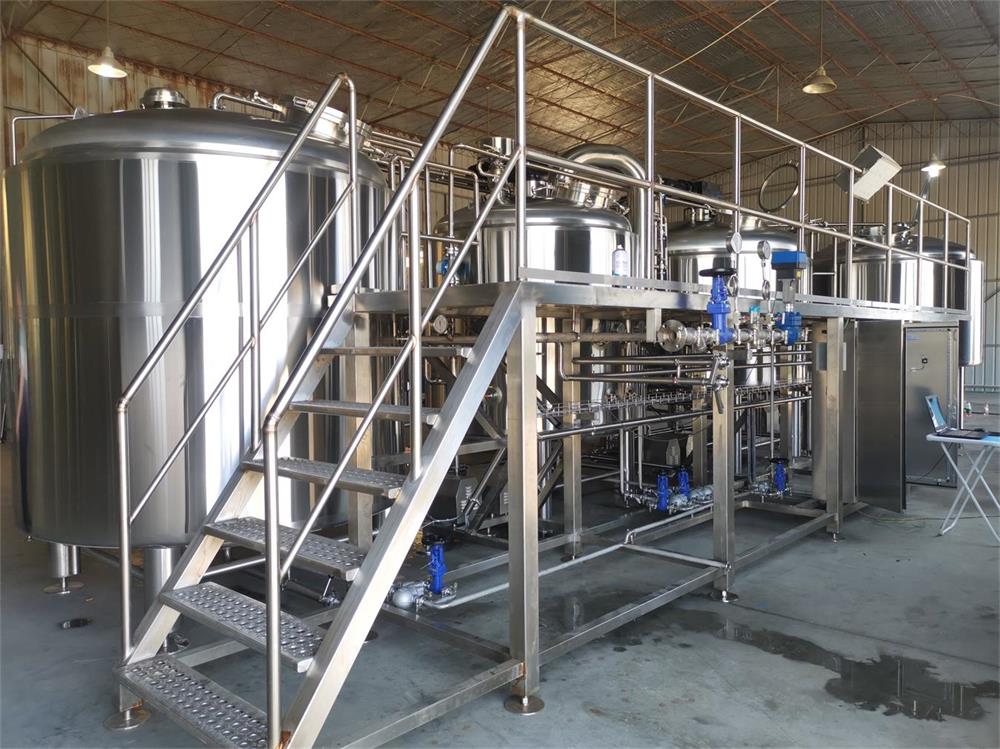

Types of Beer Making Equipment
Comparison of Homebrewing and Commercial Brewing Equipment
| Equipment Type | Homebrewing | Commercial Brewing |
|---|---|---|
| Brewing Kettle | Small, 5-20 liters | Large, 100+ liters |
| Fermentation Vessel | Glass or plastic carboys | Conical fermenters with pressure control |
| Mash Tun | DIY or small coolers | Automated systems with temperature control |
| Wort Chiller | Immersion chillers | Plate or counterflow chillers |
| Packaging Tools | Bottles, caps, basic keg systems | Automated bottling or kegging lines |
| Automation | Minimal, often manual | Highly automated with precise controls |
Materials Used in Beer Making Equipment
| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Durable, corrosion-resistant, easy to clean | More expensive |
| Glass | Non-reactive, easy to monitor fermentation visually | Breakable, heavy |
| Food-Grade Plastic | Affordable, lightweight | Prone to scratching, harder to sanitize |
| Copper | Excellent heat conductivity | High maintenance, expensive |
Brewing Process Using Equipment
Brewing involves several steps, each requiring specific equipment:
- Mashing: Grains are steeped in the mash tun to extract sugars.
- Boiling: The wort is boiled in the kettle, and hops are added for bitterness and flavor.
- Cooling: A wort chiller rapidly lowers the temperature to prepare for fermentation.
- Fermentation: The cooled wort is transferred to a fermenter, where yeast converts sugar into alcohol.
- Packaging: Finished beer is bottled or kegged for carbonation and storage.
Each of these steps can be automated or manual, depending on the scale and complexity of your setup.
Beer Making Equipment Customization
| Parameter | Options for Customization |
|---|---|
| Capacity | Home systems: 5–20 liters; Commercial: 100–10,000 liters |
| Space Requirements | Compact home systems; Dedicated brewery spaces |
| Design and Layout | Horizontal vs. vertical fermenters; modular systems |
| Automation | Manual controls to fully automated systems |
Beer Making Equipment Suppliers and Pricing
| Supplier | Price Range | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Homebrew Supply Co. | $200–$1,000 | Starter kits, beginner-friendly |
| BrewTech Industries | $2,000–$10,000 | Advanced homebrewing equipment |
| ProBrew Systems | $10,000–$200,000+ | Commercial brewing systems |
| SS Brewtech | $500–$50,000 | Stainless steel-focused equipment |
Installation, Operation, and Maintenance
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Installation | Requires plumbing, electrical setups for commercial systems |
| Operation | Understanding basic brewing principles; monitoring temperature and timing |
| Maintenance | Regular cleaning, sanitization, and inspection to prevent contamination |
How to Choose Beer Making Equipment Suppliers
When choosing suppliers, consider the following:
- Reputation: Look for reviews and testimonials to ensure reliability.
- Customization Options: Can they tailor the equipment to your needs?
- Support: Does the supplier offer installation help and after-sales service?
- Warranty: Always ask about warranties for peace of mind.
| Supplier Comparison | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Local Suppliers | Easy access, faster support | Limited range |
| International Brands | High quality, more customization options | Higher shipping costs, longer lead time |

Advantages and Limitations of Beer Making Equipment
| Aspect | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Homebrewing | Affordable, compact, DIY potential | Limited capacity |
| Commercial Systems | Scalable, efficient, high-quality output | High upfront cost, complex installation |
FAQs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What’s the best beginner setup for homebrewing? | A starter kit with a brewing kettle, fermenter, and basic tools like hydrometers. |
| How much does commercial brewing equipment cost? | Entry-level systems start at $10,000; industrial setups can exceed $200,000. |
| What’s the difference between bottling and kegging? | Bottling is affordable but labor-intensive, while kegging is quicker but requires more equipment. |