Beer Brewing Equipment: Home and Commercial Brewers
Overview of Beer Brewing Equipment
Beer brewing is an art that combines precision, science, and creativity. Whether you’re a homebrewer experimenting with small batches or a commercial brewer producing beer for thousands, the right brewing equipment makes all the difference. This guide takes a deep dive into everything you need to know about beer brewing equipment—from understanding the brewing process to selecting, maintaining, and troubleshooting key components.
We’ll break down equipment sizes, costs, materials, and customization options, so you’ll know exactly what to look for based on your brewing goals. Ever wondered how to choose between stainless steel and aluminum fermenters? Or how to design the most efficient brewing layout? We’ve got you covered.
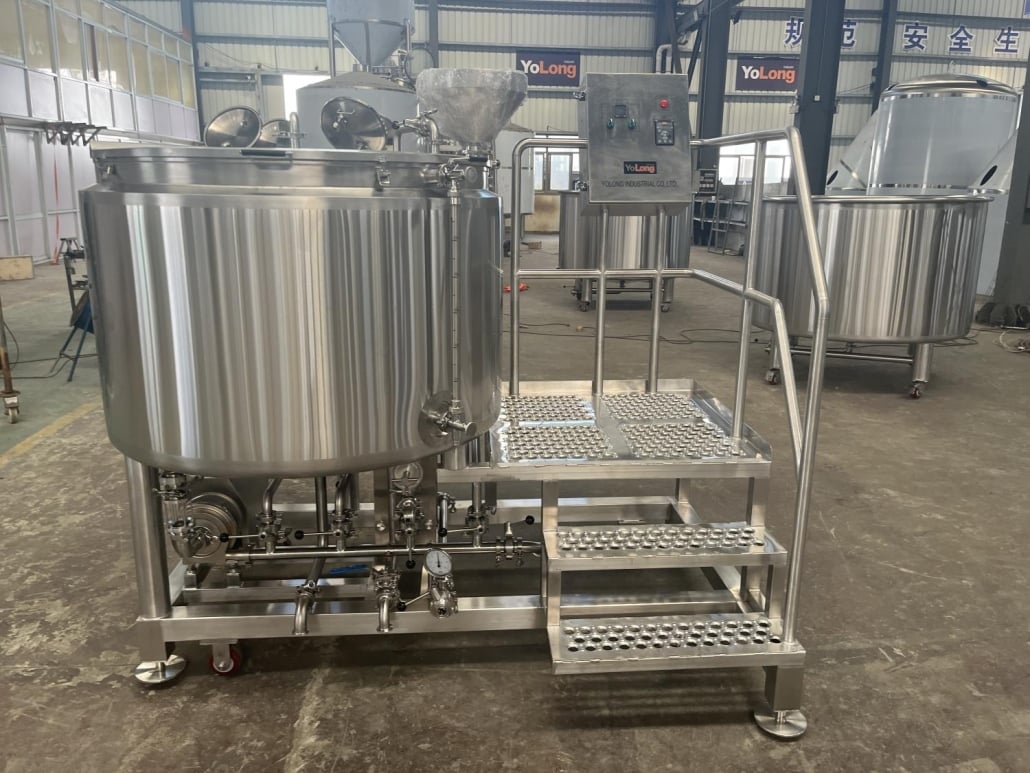

The Beer Brewing Process Explained
Brewing beer might feel overwhelming at first, but when you break it down step-by-step, the process becomes surprisingly straightforward. Here’s how it all works:
1. Malting and Milling
Beer begins with malted grains—usually barley—that are crushed to extract fermentable sugars. The milling process must be precise. Too coarse, and the sugars won’t be fully extracted; too fine, and it can clog your mash tun.
2. Mashing
Next comes mashing. The crushed grains are soaked in hot water inside a mash tun. This activates enzymes, converting the starches in the grains into fermentable sugars. Mashing equipment must maintain consistent temperature control for optimal results.
3. Lautering and Sparging
The sugary liquid (wort) is separated from the grain husks in the lautering process. Sparging involves rinsing the grains with hot water to extract any remaining sugars. A well-designed lauter tun prevents stuck sparges and inefficiency.
4. Boiling
The wort is boiled, and hops are added at various stages to provide bitterness, aroma, and flavor. High-quality kettles with proper boil efficiency are essential here.
5. Fermentation
This is where the magic happens! The cooled wort is transferred to a fermenter, and yeast is added. Over time, the yeast converts sugars into alcohol and CO2. Fermenters come in a variety of materials and designs, each affecting flavor and ease of use.
6. Conditioning and Packaging
Finally, the beer is conditioned to mellow its flavors. It can be carbonated and packaged into bottles, kegs, or cans, depending on scale and equipment.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Beer Fermenters
Fermenters are critical in the brewing process, but they’re not without their challenges. Here are some common issues and how to address them:
- Stuck Fermentation
Your beer isn’t fermenting as expected? Check the temperature and yeast health. Using high-quality fermenters with precise temperature control can help. - Contamination
Off-flavors or spoiled batches? Sanitization is key. Stainless steel fermenters are easier to clean and sanitize compared to plastic. - Pressure Buildup
If you’re using a sealed fermenter, excess CO2 can cause dangerous pressure levels. Ensure proper ventilation or pressure relief systems. - Leaks and Seals
Leaky fermenters can lead to oxidation. Check gaskets, seals, and fittings regularly.
Beer Brewing Equipment Specifications: Capacity, Design, Layout, and Customization
The following table outlines essential specifications for various types of beer brewing equipment based on capacity, layout, and customization options:
| Equipment Type | Capacity | Space Requirement | Design Features | Customization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mash Tun | 10L–5000L | Compact to Industrial | Insulated walls, temperature control | Size, material, heating method |
| Lauter Tun | 10L–5000L | Moderate | False bottom, sparging arms | Diameter, drain system |
| Boil Kettle | 10L–5000L | Moderate | Integrated burners, whirlpool options | Heating element, automation |
| Fermenters | 10L–10,000L | Moderate to Large | Conical design, pressure release valves | Material, size, cooling jackets |
| Brite Tanks | 10L–5000L | Moderate | Carbonation stones, pressure-rated designs | Volume, cooling systems |
| Kegging/Bottling Lines | Up to 50 kegs/hr | Varies | Automatic vs. manual operations | Output speed, type of packaging |
Top Suppliers and Price Ranges for Beer Brewing Equipment
Here’s a breakdown of leading suppliers and what you can expect to pay for brewing systems:
| Supplier | Equipment Offered | Price Range | Region |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ss Brewtech | Fermenters, kettles | $500–$10,000 | USA |
| Blichmann Engineering | Homebrewing equipment | $300–$5,000 | USA |
| Brewiks | Turnkey systems | $20,000–$200,000 | Europe |
| Chinese Manufacturers | Full brewing systems | $5,000–$150,000 | China |
| Microbrewery Systems | Commercial breweries | $30,000–$1,000,000 | Global |
How to Install, Operate, and Maintain Beer Brewing Equipment
Installation
Setting up brewing equipment requires precision to avoid mishaps. Proper spacing, plumbing, and power supply connections are crucial for seamless operations. Larger systems may require professional installation.
Operation
Follow these tips to operate your beer brewing equipment effectively:
- Maintain precise temperature controls during mashing and fermentation.
- Use automated controls for larger systems to improve efficiency.
- Regularly monitor for leaks or clogs in tuns and kettles.
Maintenance
Maintaining your brewing equipment ensures longevity:
- Clean and sanitize all parts regularly, especially fermenters.
- Inspect valves, hoses, and seals for wear and tear.
- Lubricate moving parts and tighten fittings as needed.
How to Choose the Right Supplier for Beer Brewing Equipment
Selecting the best supplier involves evaluating multiple parameters:
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Quality | Look for food-grade materials like 304 stainless steel. |
| Price | Compare prices across suppliers for cost efficiency. |
| Customization | Assess whether the supplier offers custom solutions. |
| Reputation | Check customer reviews and case studies. |
| Support | Evaluate after-sales service, warranty, and training. |

Pros and Cons of Different Beer Brewing Equipment Options
| Equipment | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel Tanks | Durable, easy to clean, maintains temperature | More expensive |
| Plastic Fermenters | Affordable, lightweight | Harder to clean, less durable |
| Glass Carboys | Non-reactive, visually appealing | Fragile, difficult to maneuver |
| Automatic Brew Systems | Efficient, consistent quality | Higher initial investment |
| Manual Systems | Lower cost, hands-on control | Labor-intensive, less scalable |
FAQs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the best material for fermenters? | Stainless steel is the most durable and easy to clean. |
| How much does commercial beer brewing equipment cost? | Prices range from $30,000 to over $1,000,000 depending on size. |
| How do I clean a mash tun? | Use a non-abrasive cleaner, hot water, and sanitize thoroughly. |
| Can I customize brewing equipment? | Yes, many suppliers offer customization for layout, capacity, and features. |
| What size brewery do I need? | It depends on your production goals—homebrewers may need only 20L systems. |